Generalized Iterative Closest Point (G-ICP)
먼저, setInputSource()와 setInputTarget() 함수 내부에서 어떤 일이 일어나는지 살펴본다.
사실 이 두 함수는 말그대로 입력 point cloud를 멤버 변수에 저장하는 일을 한다.
inline void setInputSource(const PointCloudSourceConstPtr& cloud) override
{
if (cloud->points.empty()) {
PCL_ERROR(
"[pcl::%s::setInputSource] Invalid or empty point cloud dataset given!\n",
getClassName().c_str());
return;
}
PointCloudSource input = *cloud;
// Set all the point.data[3] values to 1 to aid the rigid transformation
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < input.size(); ++i)
input[i].data[3] = 1.0;
pcl::IterativeClosestPoint<PointSource, PointTarget>::setInputSource(cloud);
input_covariances_.reset();
}
위의 코드를 보면 G-ICP 상의 setInputSource()은 pcl::IterativeClosestPoint의 setInputSource()을 재사용하는데, 해당 함수는 아래와 같이 정의되어 있다.
void setInputSource(const PointCloudSourceConstPtr& cloud) override
{
Registration<PointSource, PointTarget, Scalar>::setInputSource(cloud);
const auto fields = pcl::getFields<PointSource>();
source_has_normals_ = false;
for (const auto& field : fields) {
if (field.name == "x")
x_idx_offset_ = field.offset;
else if (field.name == "y")
y_idx_offset_ = field.offset;
else if (field.name == "z")
z_idx_offset_ = field.offset;
else if (field.name == "normal_x") {
source_has_normals_ = true;
nx_idx_offset_ = field.offset;
}
else if (field.name == "normal_y") {
source_has_normals_ = true;
ny_idx_offset_ = field.offset;
}
else if (field.name == "normal_z") {
source_has_normals_ = true;
nz_idx_offset_ = field.offset;
}
}
}
위에서도 마찬가지로 Registration의 setInputSource() 함수를 가져오고:
template <typename PointSource, typename PointTarget, typename Scalar>
inline void
Registration<PointSource, PointTarget, Scalar>::setInputSource(
const PointCloudSourceConstPtr& cloud)
{
if (cloud->points.empty()) {
PCL_ERROR("[pcl::%s::setInputSource] Invalid or empty point cloud dataset given!\n",
getClassName().c_str());
return;
}
source_cloud_updated_ = true;
PCLBase<PointSource>::setInputCloud(cloud);
}
최종적으로 제일 밑단에 있는 PCLBase 클래스의 setInputCloud() 함수를 통해 입력값을 input_에 저장한다.
template <typename PointT> void
pcl::PCLBase<PointT>::setInputCloud (const PointCloudConstPtr &cloud)
{
input_ = cloud;
}
즉, G-ICP의 코드는 아래와 같이 상속이 되어 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
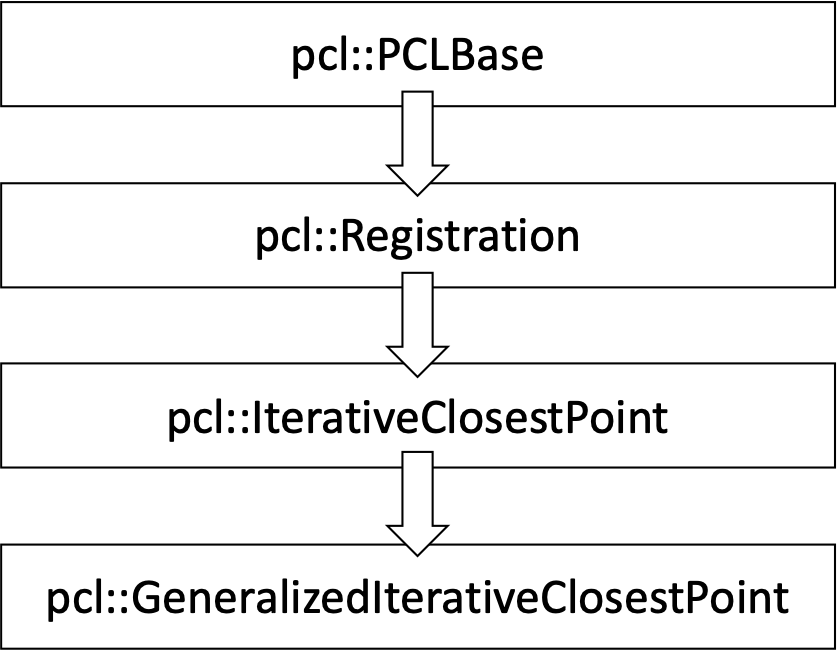
이 구조를 알아두는 것은 생각보다 중요하다. 왜냐하면 새로운 registration 알고리즘을 구현할 때 pcl::Registration 클래스를 상속받아서 코드를 구현하게 되면 PCL의 생태계와 친화적이면서도, 기본적으로 registration을 할 때 필요한 structure가 이미 잘 짜여져 있기 때문에 코드 작성할 시간을 단축시켜 준다.
이와 마찬가지로, setInputTarget()도 상속을 통해 이루어져 있는 것을 확인 할 수 있다:
inline void setInputTarget(const PointCloudTargetConstPtr& target) override
{
pcl::IterativeClosestPoint<PointSource, PointTarget>::setInputTarget(target);
target_covariances_.reset();
}
setInputTarget()은 pcl::IterativeClosestPoint의 setInputTarget()을 재사용하는데, 해당 함수는 아래와 같이 정의되어 있다.
void setInputTarget(const PointCloudTargetConstPtr& cloud) override
{
Registration<PointSource, PointTarget, Scalar>::setInputTarget(cloud);
const auto fields = pcl::getFields<PointSource>();
target_has_normals_ = false;
for (const auto& field : fields) {
if (field.name == "normal_x" || field.name == "normal_y" ||
field.name == "normal_z") {
target_has_normals_ = true;
break;
}
}
}
최종적으로 Registration의 setInputTarget() 함수에서 입력된 cloud를 target_에 저장한다.
template <typename PointSource, typename PointTarget, typename Scalar>
inline void
Registration<PointSource, PointTarget, Scalar>::setInputTarget(
const PointCloudTargetConstPtr& cloud)
{
if (cloud->points.empty()) {
PCL_ERROR("[pcl::%s::setInputTarget] Invalid or empty point cloud dataset given!\n",
getClassName().c_str());
return;
}
target_ = cloud;
target_cloud_updated_ = true;
}
즉 정리하자면, 이 setInputSource()와 setInputTarget() 함수들의 역할은 크게 네가지라고 볼 수 있다
- i) 비어진 point cloud가 주어진 건 아닌지 check
- ii) Point cloud의 point에 대응하는 normal이 이미 계산되어 있는지 check
- iii) source cloud는
input_, target cloud는target_이라는 멤버변수에 할당 - iv) covariance를 지니고 있는 vector pointer들 리셋