Iterative Closest Point (ICP)
SLAM 분야에서 흔히 registration == Iterative Closest Point (ICP)라고 일반적으로 취급할 만큼, ICP는 local registrtaion 중에서 가장 유명한 알고리즘입니다.
ICP는 말 그대로 iterative하게 가장 가까운 point를 찾는것을 반복하면서 optimization이 시행되는데, 한 iteration 마다 두 개의 step으로 구성되어 있습니다. Registration에서는 통상적으로 주어진 두 point cloud pair를 각각 source와 target으로 부르는데, 이 source가 target에 다가가는 transformation matrix를 구해주는 함수입니다.
앞서 말한 두 step은 아래와 같습니다.
-
- 현재 주어진 source 각 point 별 가장 가까운 target point를 찾는다 (knn에서 k=1로 해서 가장 가까운 것을 찾음).
-
- 그 포인트 쌍들을 기반으로 transformation matrix를 incremental하게 추정한다.
이 1->2->1->2…하는 식으로 반복하여 더 이상 transformation matrix의 변화(epsilon)가 0에 근접하면 optimization을 종료합니다.
How to Use (77번 째 줄부터)
파라미터 세팅
ICP를 할 때 크게 주의해야할 파라미터 세팅은 아래와 같이 세개가 있습니다.
setMaxCorrespondenceDistance()setTransformationEpsilon()setMaximumIterations()
결과값 return 받기
getFinalTransformation(): src를 transform한 결과를 받을 수 있습니다.getFitnessScore(): 각 point pair별 거리의 제곱의 평균이 나옵니다 (작을수록 더 registration이 잘되었다고 볼 수 있음)hasConverged(): 수렴하면true리턴
여기서 주의하실 점은 hasConverged() 함수로 registration이 수렴했는지 안 했는지 판별하는 것은 좋은 선택이 아니라는 것입니다. 왜냐하면 hasConverged()는 registration이 진짜 true, best solution에 갔는지의 여부는 알바 아니고, 각 transformation의 epsilon이 작기만 하면 true를 리턴하기 때문에, setMaximumIterations()의 크기가 충분히 거진 100% true를 리턴하기 때문에 변별력이 없습니다. 따라서 ICP를 사용하실 때는 getFitnessScore() 함수를 이용하는 것이 좋습니다.
즉, score가 fit한지 아닌지 score 값이 어느 정도 작은 경우는 두 point cloud가 충분히 잘 포개졌다는 의미이기 때문에 잘 수렴했다고 간주할 수 있습니다.
하지만 getFitnessScore()도 만능은 아닌데, 왜냐하면 두 point cloud의 overlap된 정도가 적은 상태에서 fitness score를 구하게 되면 수렴을 잘 했더라도 큰 fitness score를 보이기 때문입니다.
저 Fitness score는 두 point cloud가 잘 포개질수록 낮은 값을 제공한다고 말했는데,
overlap 자체가 적은 경우에는 src/tgt의 overlap 이외의 부분으로부터 가장 가까운 tgt/src point가 어느정도 거리가 떨어져 있습니다.
따라서 이 getFitnessScore()를 너무 타이트하게 잡게 되면, overlap된 영역이 작은 두 point cloud도 잘못된 registration이라고 판단되어 registration이 잘 됐음에도 불구하고 걸러질 수도 있습니다.
그러니 filtering할 때는 꼭 주의해서 filtering을 해야합니다!
결과
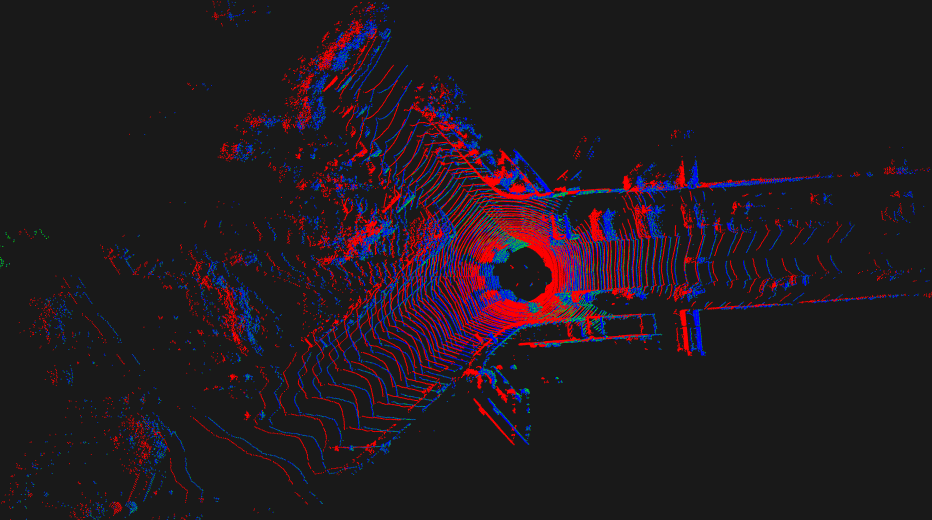
보시는 것처럼, 앞으로 2m transformation을 인위적으로 한것을 따라간 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
하지만 생각보다 저의 개인적으로는 이런 도심환경이나 실내 환경에서 registration을 할 때는 ICP보다 G-ICP를 사용하는 것이 훨씬 낫습니다. (이 부분은 단언코 말씀드릴 수 있습니다)
Point Cloud Library Tutorial 시리즈입니다.
모든 코드는 이 레포지토리에 있고, ros package로 구성되어 있어 build하여 직접 돌려보실 수 있습니다
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 0. Tutorial 및 기본 사용법
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 1. Ptr, ConstPtr의 완벽 이해 (1) shared_ptr
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 1. Ptr, ConstPtr의 완벽 이해 (2) Ptr in PCL
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 1. Ptr, ConstPtr의 완벽 이해 (3) Ptr in 클래스 멤버변수
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 2. 형변환 - toROSMsg, fromROSMsg
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 3. Transformation
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 4. Viewer로 visualization하는 법
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 5. Voxelization
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 6. PassThrough
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 7. Statistical Outlier Removal
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 8. KdTree를 활용한 Radius Search
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 9. KdTree를 활용한 K-nearest Neighbor Search (KNN)
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 10. Normal Estimation
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 11. Iterative Closest Point (ICP)
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 12. Generalized Iterative Closest Point (G-ICP)
- ROS Point Cloud Library (PCL) - 13. getVector3fMap()을 통한 효율적인 복사